Radware DefensePro: Reports and Statistics
Last Update 21/3/2023
Radware DefensePro protects network traffic from attacks and performs behavioural traffic analysis. It automatically detects and blocks attacks in real-time by continuously learning static network traffic. Customers who use this security solution for their services can view detailed information about filtered attacks in the Network services tab in Customer Administration.
Section Description and Report Filter
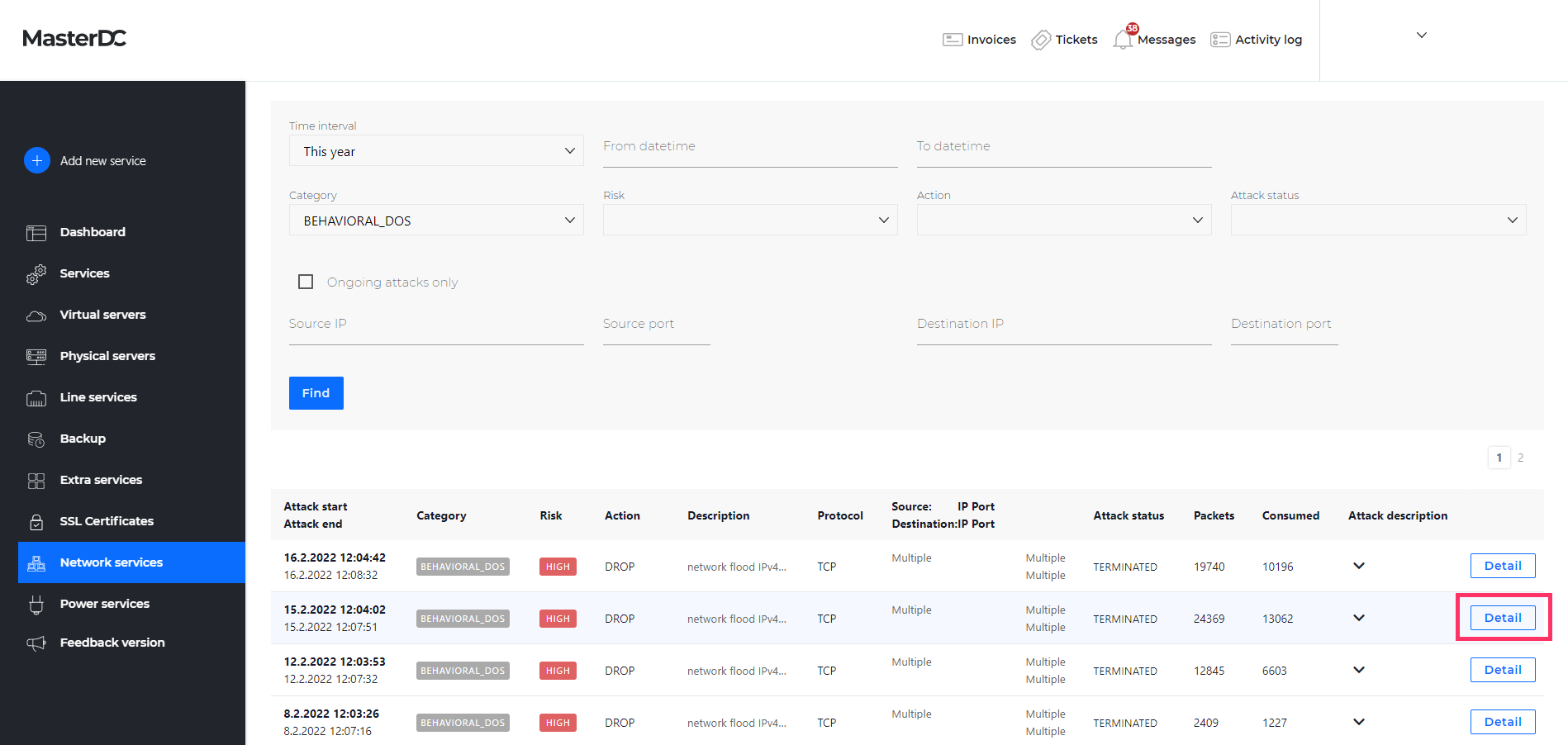
Log in to Customer Administration at https://admin.masterdc.com/en/. Once logged in, select Network services from the left-hand side menu. Here, you can find the Radware Network Protection service.
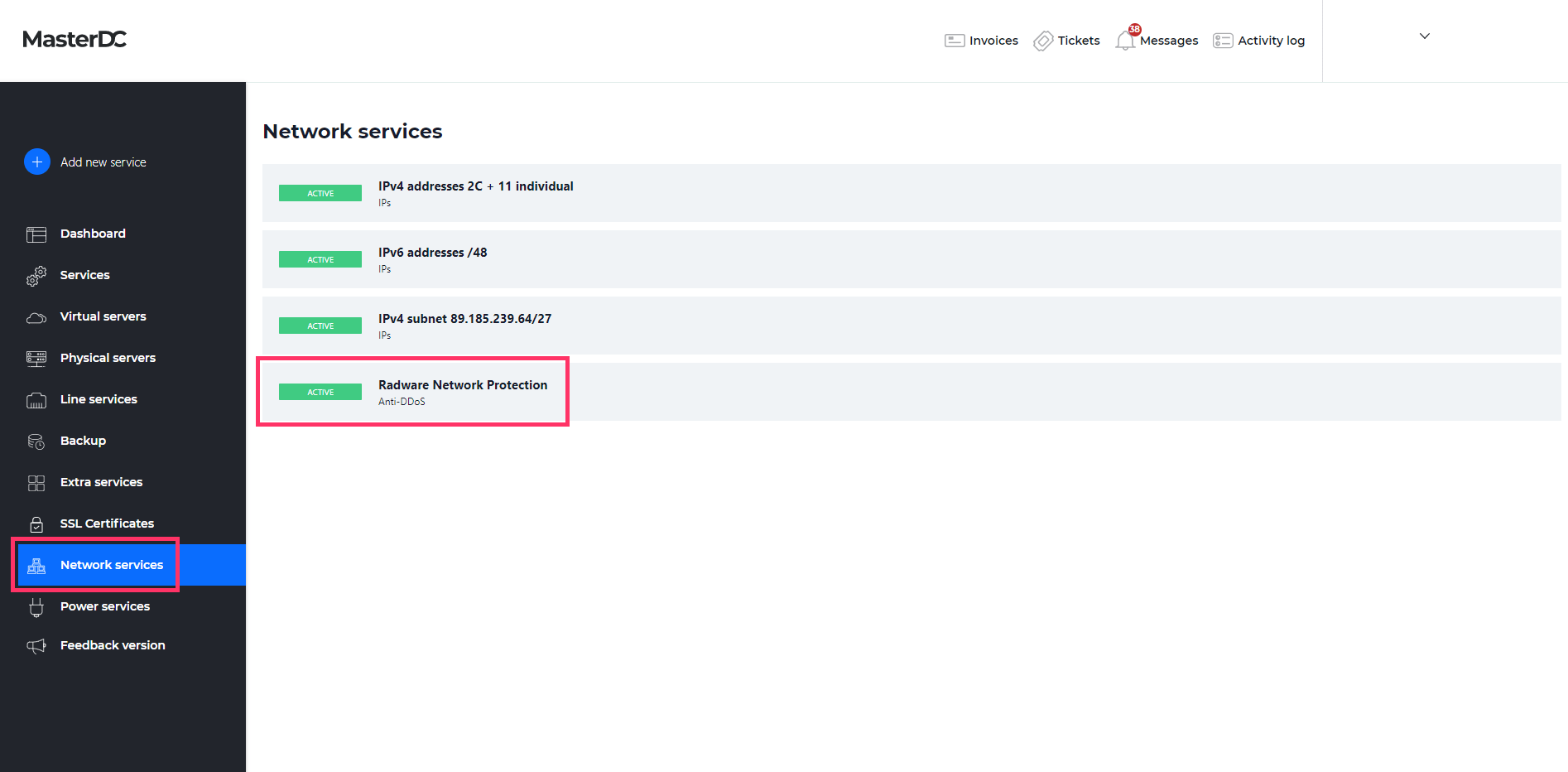
Selecting this item will show you the service details and payment information. Next, navigate to the Statistics tab, where you will find options for filtering out blocked or even occurring attacks.
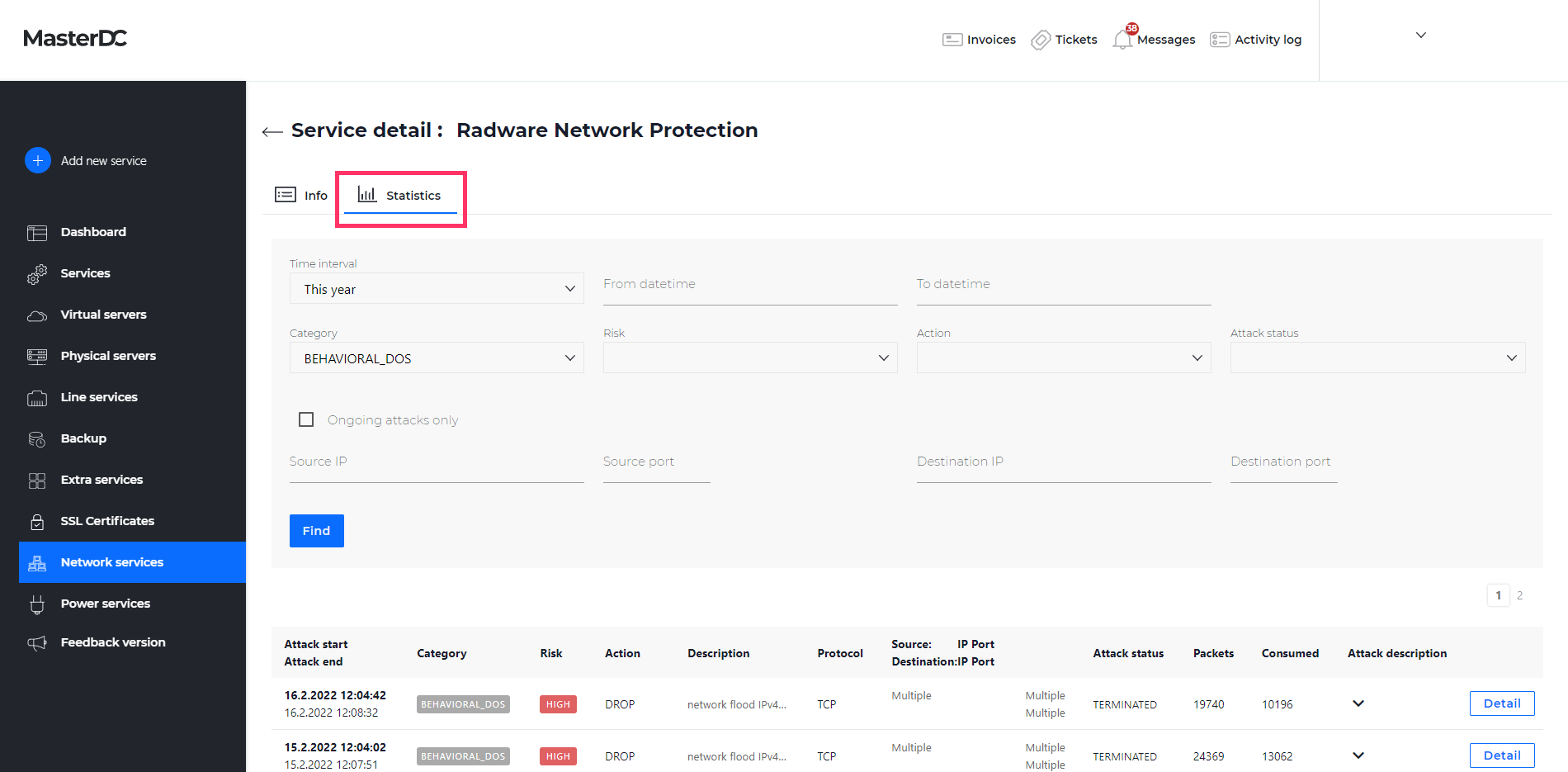
Filtering
- Time Interval/From Date-To Date – The period of which you want to list the attacks.
- Category – The type of attacks.
- Risk – Attack risk classification.
- Action – Any action taken against the attacks, description in Table 1.
- Attack Status – Information about the attack’s current status, description in Table 2.
- Source IP and Port – The attack’s source IP.
- Destination IP and Port – The attack destination IP.
| Action | Description |
| Bypass | DefensePro does not protect against this attack but rather sends its data out of the device and may report it. |
| Challenge | DefensePro challenges the packet. |
| Destination_Reset | DefensePro sends a TCP-Reset packet to the destination IP address and port. |
| Drop | DefensePro discards the packet. |
| Drop_Quarantine | DefensePro discards the traffic and adds the destination to the Web quarantine. |
| Forward | DefensePro continues to process the traffic and eventually forwards the packet to its destination. |
| http_200_Ok | DefensePro sends a 200 OK response using a predefined page and leaves the server-side connection open. |
| http_200_Ok_Reset_Destination | DefensePro sends a 200 OK response using a predefined page and sends a TCP-Reset packet to the server-side to close the connection. |
| http_403_Forbidden | DefensePro sends a 403 Forbidden response using a predefined page and leaves the server-side connection open. |
| http_403_Forbidden_Reset_Dest | DefensePro sends a 403 Forbidden response using a predefined page and sends a TCP-Reset packet to the server-side to close the connection. |
| Proxy | Proxy |
| Quarantine | DefensePro adds the destination to the Web quarantine. |
| Source_Destination | DefensePro sends a TCP-Reset packet to the packet destination IP address. |
| Source_Reset | DefensePro sends a TCP-Reset packet to the destination IP address and port. |
Table 1: Description of Actions Taken Against Attacks.
| Attack Status | Description |
| Occured | Relevant for signature-based attacks, each packet matched with signatures was reported as an attack and dropped. |
| Ongoing | The attack is currently taking place, that is, the time between Started and Terminated (for attacks that contain multiple security events, such as DoS, Scans, etc.). |
| Started | An attack containing more than one security event has been detected (Some attacks contain multiple security events, such as DoS, Scans, etc.). |
| Terminated | No more packets match the characteristics of the attack, and the device reports that the attack has ended. |
Table 2: Description of Attack Status.
Once the attacks have been filtered, you will see a detailed description of the threat alongside the basic parameters, including recommendations on what steps to take to eliminate future risks.
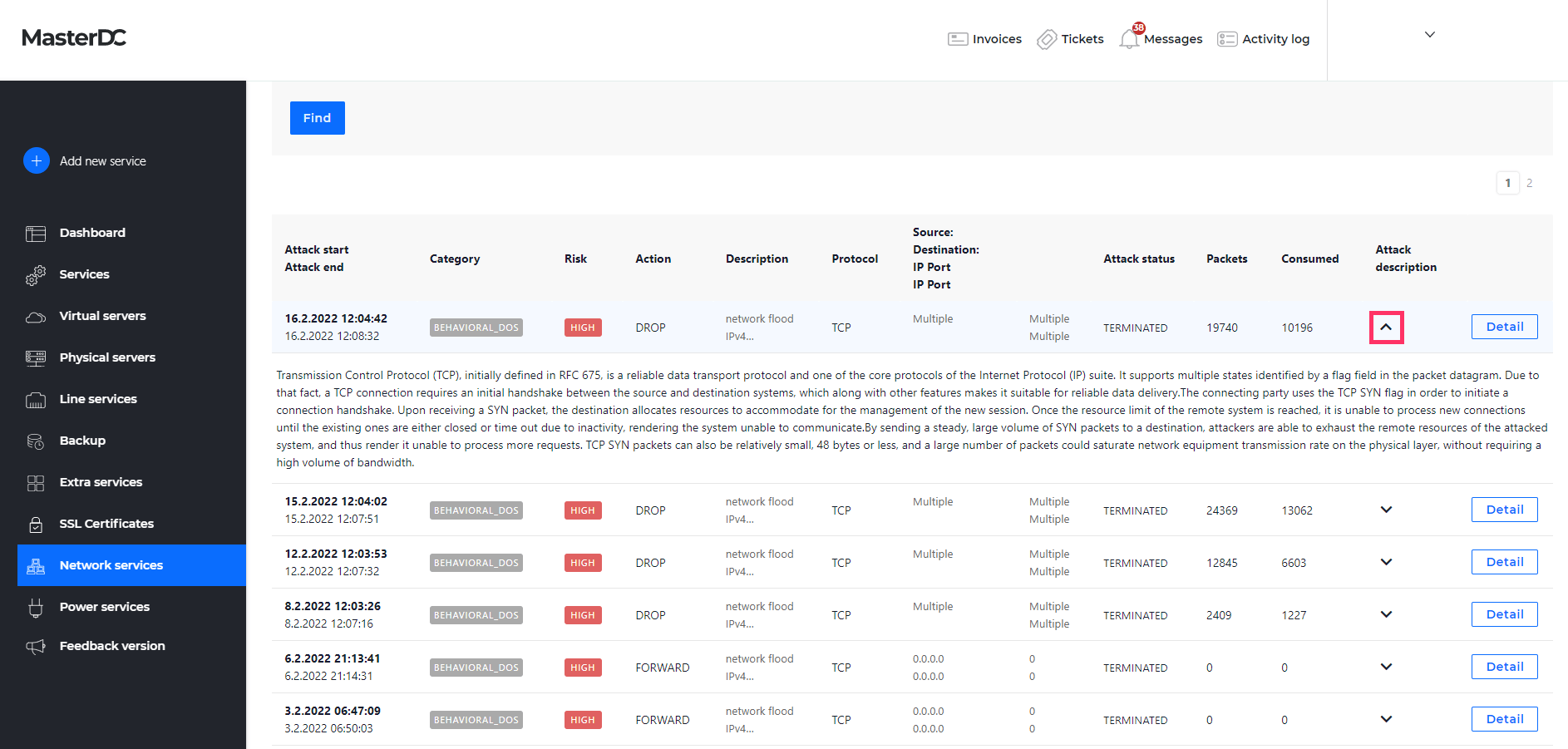
Behavioural DoS Attacks
For behavioural DoS attacks, you can view a more detailed report, including the footprint (i.e. automatically generated filter to attack removal), characteristics, and attack graph. Click on the Detail button on the BDoS in the listing to display these details.
Footprint Tab
The Footprint tab contains an automatically generated attack traffic filter generated by the DefensePro behavioural module in the following form:
Version: 1
[ OR vlan-tag=1325,1323,] AND [ AND destination-ip=XXX.XXX.XXX.XX, AND ttl=51,54,]Table 3 below explains the different values of this figure.
| Value | Meaning |
| Protocol | The protocol that the attack uses or used. |
| Source L4 Port | The source L4 port that the attack uses or used. |
| Physical Port | The physical port that the attack uses or used. |
| Packet Count | The packet-count of the attack. |
| Volume (Kbits) | The volume in Kbits that the attack uses or used. |
| VLAN Tag/Context | The VLAN tag value or Context Group in the policy that handled the attack. The VLAN tag is unavailable when the value is N/A or 0 (zero). |
| MPLS RD | The Multi-Protocol Label Switching Route Distinguisher in the policy that handled the attack. The value N/A or 0 (zero) in this field indicates that the MPLS RD is unavailable. |
| Device IP | The device IP address that the attack uses or used. |
| TTL | The TTL that the attack uses or used. |
| L4 Checksum | The L4 checksum that the attack uses or used. |
| TCP Sequence Number | The TCP sequence number that the attack uses or used. |
| IP ID Number | The IP ID number that the attack uses or used. |
| Fragmentation Offset | The fragmentation offset that the attack uses or used. |
| Fragmentation Flag | The fragmentation flag that the attack uses or used. Zero (0) indicates that fragmentation is allowed. One (1) indicates that fragmentation is not allowed. |
| Flow Label | (IPv6 only) The flow label that the attack uses or used. |
| ToS | The ToS that the attack uses or used. |
| Packet Size | The packet size that the attack uses or used. |
| ICMP Message Type | The ICMP message type that the attack uses or used (this is displayed only if the protocol is ICMP). |
| Source IP | The source IP address that the attack uses or used. |
| Destination IP | The destination IP address that the attack uses or used. |
| Source Ports | The source ports that the attack uses or used. |
| Destination Ports | The destination port that the attack uses or used. |
| DNS ID | The DNS ID that the attack uses or used. |
| DNS Query | The DNS query that the attack uses or used. |
| DNS Query Count | The DNS query count that the attack uses or used. |
Table 3: Footprint Value Explanation.
Characteristics Tab
Additional attack details are in the Characteristics tab, which overlaps with some of the values in Table 3. However, the tab also contains information about the attack length and strength or the current protection process state. These values are described in Table 4.
| Value | Description |
| Avg Burst Duration | In hh:mm:ss format, the average duration of the bursts. |
| Avg Burst Rate | The average rate in Kbps of the bursts. |
| Avg Time Between Bursts | The average time between separate bursts in hh:mm:ss format. |
| Controller State | The state of the protection process; values: footprint analysis, footprint-applied, burst-footprint-blocking, footprint-is-overblocking, non-attack (explanation in the “Footprint Generation States” below). |
| Current Burst Number | The number of bursts since the start of the attack. |
| Burst Active | Values YES – Attack Active, NO – Attack Non-Active. |
| Max Burst Rate | The rate in Kbps of the biggest burst of the attack. |
| Version | Attack version. |
Table 4: Characteristics Tab, Values Description.
Footprint Generation States
- Footprint Analysis – BDoS protection has detected an attack and is currently generating an attack footprint.
- Footprint-Applied – BDoS protection is blocking the attack based on the generated footprint. BDoS protection optimizes the footprint rule through a closed-feedback loop operation, achieving the narrowest effective mitigation rule.
- Burst-Footprint-Blocking – BDoS protection blocks the burst attack based on the footprint generated by the previous states. This state remains until the burst attack terminates or the specified Maximum Burst-Attack Period is reached.
- Footprint-Is-Overblocking – BDoS protection started blocking the attack but stopped three times after identifying an overblocking situation. This state remains for 10 minutes, after which BDoS protection generates and implements a new footprint.
- Non-Attack – Nothing was blocked because the traffic was not an attack. No footprint was detected, or the blocking strictness level was not met.
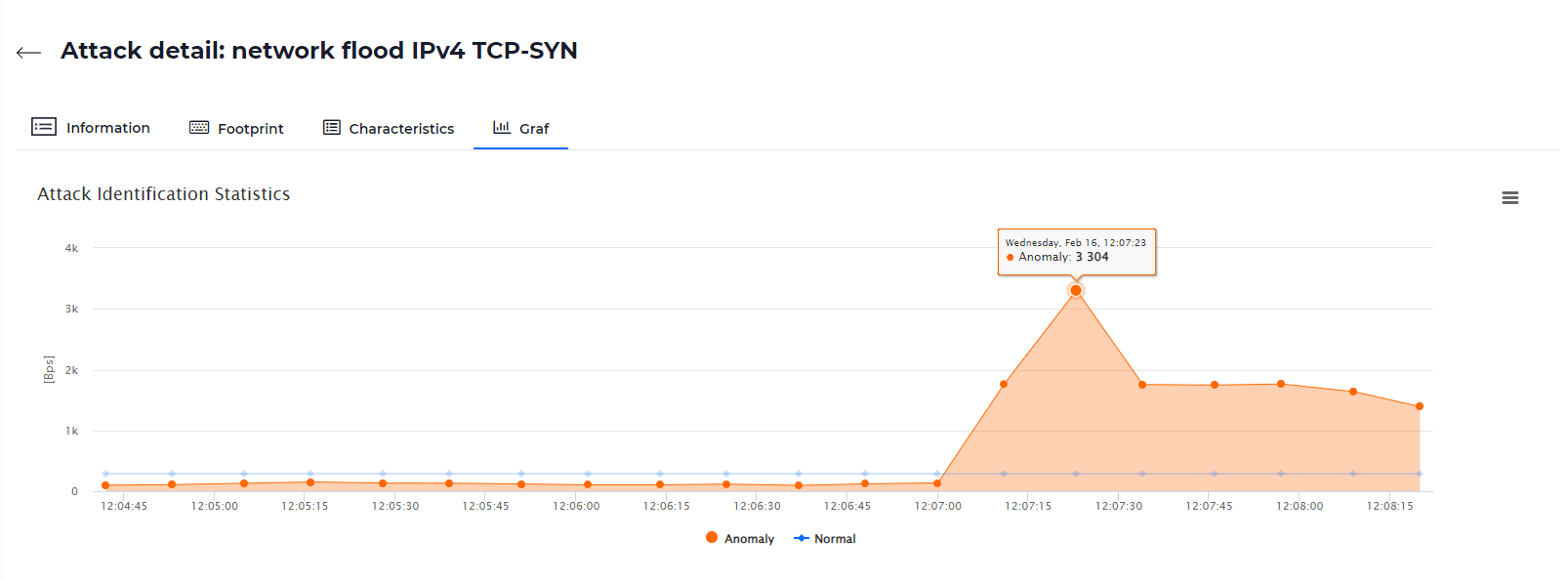
Attack Graph
In the last tab, you will find a generated graphical representation of the attack compared to normal network traffic. You can download the graph in PNG, JPEG, PDF, or SVG format.