What is disaster recovery and why you should plan it
Disasters of any kind occur at any time and the best way to respond to them is through prevention. So, what is disaster recovery? the essence of what we know as business continuity. A disaster recovery plan is a shield to protect the companies' infrastructure in the event of natural disasters, cyber attacks or any other type of risk that compromises the stability of the business services. If you still do not have a disaster recovery plan, let us explain to you why it is important and why you should start considering to design one.

What is disaster recovery?
As we mentioned before, the term disaster recovery is associated with what in the IT environment is known as business continuity. Both terms are often confused with each other, but their function is complimentary.
Disaster recovery is an essential part of the processes carried out by the business continuity system since it is responsible for restoring and maintaining the company’s services if a disaster occurs.
Why is it important to have a disaster recovery plan?
More than ever, companies are becoming less tolerant of downtime since this could mean losses in millions of dollars and even the end of the business overall.
This is the major reason why organizations are investing more resources to achieve a high level of business continuity.
According to Gartner 70% of organizations that have gone down for 96 hours never recovered.
A disaster recovery plan ensures that the infrastructure in your company including applications will be always available even if a disaster occurs.
Also, a disaster recovery plan can increase your business credibility because you can guarantee the continuity of the services to your customers. That will give you a competitive advantage.
80% of companies that suffer a major disaster and don’t have any contingency plan planning go into liquidation within 18 months. SDN Communications.
Do you know that...?
Master Internet can help you build a Disaster Recovery strategy. We offer the opportunity to develop and implement a Disaster Recovery plan for all types of hosting services as well as for the internal infrastructure.
Who participates in a disaster recovery plan?
Basically, the members of the IT department should be able to design a disaster recovery plan.
Before the plan is approved by the company, it must be tested to detect possible faults. A key part of the plan is to assign a disaster response team and make a list of people to be contacted in case the plan is implemented.
For instance, the plan must be known not only by the IT staff but also by other areas of the company so that everyone knows what to do in the event of a contingency.
From the CEO to the managers and the human resources department, they should know the procedures of the disaster recovery plan.
Likewise, information about the disaster recovery plan must be disseminated among external providers who participate in tasks such as software and data backup to have effective coordination when a disaster occurs.
How does a disaster recovery plan work?
When a disaster occurs, the first steps of the reaction team should concentrate on making a quick analysis of the situation to know what hardware, software, data or systems were affected and, therefore, decide which phase of the recovery plan should be executed.
When the contingency ends, an analysis of the execution of the plan must be made again to detect its vulnerabilities and strengths and make the necessary improvements.
Even if there is no emergency, the disaster recovery plan should be reviewed and updated periodically to improve it. Remember that threats and companies evolve constantly and any plan can become obsolete if it is not adapted with the right frequency.
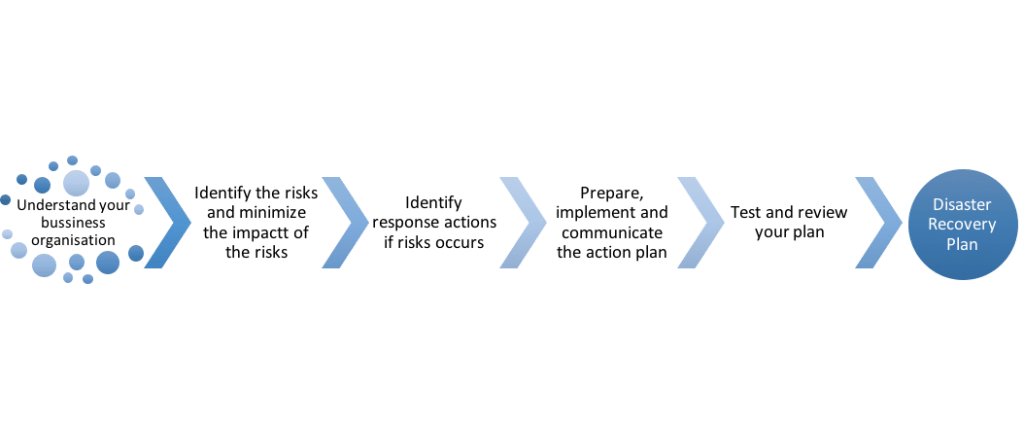
Steps to design a disaster recovery plan.
Tips for designing a disaster recovery plan
There are hundreds of templates on the Internet dedicated to making a disaster recovery plan, but keep in mind that every template you use must be adapted to the needs of your company’s infrastructure. As general advice to design a disaster recovery plan, we suggest the following steps:
- Make a diagram of the entire IT network and the recovery site. The diagram should include the instructions to start and access the recovery site.
- List all the software that is hosted on your system, as well as all the license keys that will be necessary for the restore point.
- Define the objectives and summarize the complete plan.
- Make a step by step diagram of actions to follow during the action plan.
- Definition of the RPO (Objective of the recovery point) and RTO (Objective of the recovery time) within the plan.
- Consider insurance coverage to face financial and legal problems.
- List of priority contacts within the disaster recovery team.
In addition to these recommendations, it’s always better to let professionals assist you in creating your own disaster recovery plan.
What are RPO and RTO?
The RPO determines the recovery point of the files that will be restored. This means the last point of stability prior to the disaster that is chosen to restore the system.
For example, if you choose an RPO of 1 hour, the system will back up the data every hour to apply the RPO you choose in case of a disaster.
The RTO is the maximum amount of time that the system will take to recover after a disaster. An RTO can be measured in seconds, minutes, hours or days.
According to the RTO, you must define the type of backup for recovery. For example, if the RTO is one hour, backup of redundant data on external hard drives can work as the best option.
But if the RTO is set up for several days, the offsite storage on a remote web server can work better.



