VPS in Central Europe: The Ultimate Guide How To Choose the Right VPS Hosting
When choosing a VPS, you should always consider what market you want to focus on first. For example, the location of the virtual server is often underestimated when, in reality, it is extremely important to the latency level and legislation side of the business. Find out why and what other aspects you should consider before choosing a VPS.

One could think that choosing a virtual server is much easier than choosing a physical server. However, there are many differences among the individual VPSs. Therefore, your choice should not be rushed.
While renting a dedicated (physical) server means that customers have the entire physical hardware at their disposal, customers only use a particular part of the physical hardware resources in the case of a virtual server. A physical server is divided by virtualisation into several virtual machines that are isolated from each other and function as separate servers.
This scenario is ideal for less demanding projects that do not depend on stability and high availability. On the other hand, if you are looking for a virtual environment with higher reliability, the cloud is the route to take since it works on the same principle but is usually more stable. This, of course, differs from provider to provider.
Configure and Buy a VPS Server in Seconds
Customise your virtual server to fit your project perfectly. Choose one of the available platforms, and select the required RAM size, CPU, and preferred operating system. Then, you can set up your VPS immediately and online.
Choosing a VPS Provider
Fact: when deciding which VPS to choose and which provider to cooperate with, it is a much more complex process – you have to consider the technical background of the data centre facilities, the virtualisation technologies, and the specific provider’s reputation. Another thing you should be interested in is the location of the data centre where your VPS will be hosted.
You will have to undergo some research, but here are some tips that should help you figure out the priorities to focus on.
1. 24/7 Support should be Standard
When a problem occurs on your server, you want it solved as quickly as possible. At that point, you need to have a professional and reliable person from the provider’s side who will answer your request in a short time and who will immediately help you with your issue. However, make sure the support also uses a language you understand – it is definitely not a standard for every provider to have support members who will guide you in English.
2. Availability of IT Experts
Technical support is not always enough. There could be a time when you need the help of someone deeply knowledgeable in a specific field. Therefore, it is a good sign if the technical support closely cooperates with a team of sysadmins. That means that when anything goes wrong, the support member just calls the administrator, who will solve problems requiring higher expertise.
3. Security and Monitoring
The number one priority should be data centre security. In case of fire or theft, you may experience the unpleasant fact that virtual servers are not entirely virtual but can be physically damaged or stolen as well. Is the data centre well equipped to overcome common disasters? What happens if a stranger wants to enter the server room? Is physical security present at all times, and is the data centre monitored? These are the questions you should be asking.
Location is Important – Be Close to Your Customers
Of course, you do not need to access the physical hardware when using virtual server hosting. However, despite this fact, the choice of location is still important since it has a considerable impact on the latency level.
For instance, if you plan to expand your business to Europe, hosting the servers for this market in America does not make any sense. This is because if there is a significant distance between the client and the server, the latency increases. High latency results in a longer loading time and makes it more difficult for users to click through the website. This, for example, can increase the probability of customers not completing the purchase.
Therefore, central Europe is the perfect place to host servers if you are entering the European market. Although, most likely, you will not find any giant providers. Nevertheless, the local ones can usually offer a quicker response and a more personal approach from the support team. Furthermore, thanks to intense competition in the European environment in hosting, the technological standard is pretty high compared to the price. As a result, you potentially get excellent value for money.
VPS Hosting in Central Europe Helps to Comply with EU Privacy Laws and Regulations
When Europe’s data privacy and security laws, the so-called GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), was put into effect on May 25, 2018, many organisations and enterprises in the public and private sector worldwide struggled, and some of them are still incapable of complying with it today.
In 2020, the Court of Justice of the European Union announced that any cloud services hosted in the US could not cope with the EU privacy laws. Therefore, cloud-based services are obligated not to transfer personal data from any website operating within the EU or websites with traffic coming from EU visitors to the USA, UK, India, and other states outside the EU. In addition, high fees are charged when breaching these requirements.
The best solution to fulfil the EU’s rules is to host your server in states that have a comparable level of privacy protection and are certified by the EU, such as Switzerland, or to host right in one of the European Union countries, e.g., the Czech Republic. Of course, this applies to data and metadata processing as well. For these reasons, make sure the provider possesses all the security certifications or compliance standards, for example, ISO.
How to Choose a VPS
Speaking of an actual virtual server, you should be especially interested in the hardware parameters and the type of virtualisation. In addition, taking a look at the range of available add-ons, especially for cyber security and operation management levels, is also a clever idea.
Hardware Parameters
The essential parameters consist of the number of CPUs, RAM, and hard disk size. However, the specific configuration will depend on the project requirements. Unquestionably, more demanding projects and applications need more resources. Unfortunately, there is no key to deciding; the best option is to discuss your situation with the provider.
Be aware that not every provider enables a change of parameters as you go. Thus, think ahead when setting up the exact configuration and estimate what parameters your application will need in several months or years. Then, discuss these requirements with the provider and ask about the possibilities and conditions of scaling.
When it comes to hard disks, as it stands, most users choose fast SSD disks, which can have modern NVMe and PCIe interfaces and demonstrably have better performance.
The server hardware itself is equally important. Powerful hardware from a reliable vendor can lower the number of physical server failures (on which the virtual machine runs) and data loss risks.
Type of Virtualisation
The virtualisation type is crucial for the server features. Although the variety of virtualisation is quite wide, for basic orientation, it should be enough to know the two main ones – full (native) virtualisation and lightweight virtualisation.
In the case of full virtualisation, the operation and monitoring of the virtual servers are managed directly on the hypervisor level, which is the main component of the virtualisation.
The hypervisor allows the virtualisation of hardware capacities and the creation of individual virtual machines (or complex clusters). In addition, the operating system stands under the hypervisor. As a result, each virtual machine can run a different unmodified operating system – the main benefit of full virtualisation.
On the contrary, the overhead costs are pretty high since the operation of the hypervisor itself usually consumes up to 20% of the physical server’s power. Virtual servers running on KVM or Hyper-V platforms are examples of full virtualisation technology.
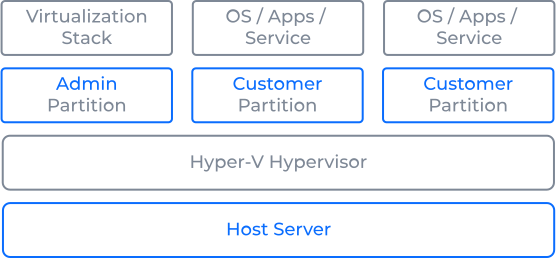
Architecture of Native Virtualisation with the Use of Hyper-V Hypervisor
Lightweight virtualisation creates so-called “containers”. These containers represent virtual machines that run on one physical server. However, unlike full virtualisation, they share the core operating system. The advantage of virtualisation on the level of an operating system is the better usage of computing power. In addition, each container can be isolated and deployed in a different environment. Examples of this virtualisation are LXC or Docker.
| KVM | Hyper-V | LXC | |
| Virtualisation Type | Full | Full | Lightweight |
| Operating System | Linux | Windows | Linux |
| Nested Virtualisation | YES | YES | NO |
| Containerisation (Docker) | YES | YES | NO |
| Administration | YES | YES | NO |
| Kernel Module | YES | YES | NO |
| Kernel Version | Private | Private | Shared |
KVM and Hyper-V – full virtualisation available in MasterDC compared to lightweight LXC virtualisation.
Available Add-Ons and Administration Options
Getting a virtual server only is not enough. You also need to backup and protect your data. Therefore, the best way is to purchase backup space on a separate server. Some level of monitoring should be enough to start with server security. Nevertheless, consider using DDoS protection if you want real cybersecurity since these attacks are becoming more frequent every year.
Otherwise, with the increasing popularity of microservices architecture, you may be interested in the possibility of Docker deployment. Indeed, you can use Docker for containerisation; however, make sure your VPS runs on a full virtualisation platform.
Some variants of virtual servers can be managed by professional administrators as well. This mode is ideal for those who want to save time on the technical side of the business since administration usually includes the complete setup of the server, regular updates of the system, backups, or security patches.
Remember that your business will grow, and you should be ready for that. You want to be able to scale your resources whenever you need and have more sophisticated routes to take, e.g., migrate to the cloud or have a cluster designed.
Ask the Provider for Help
The best advice always comes from a professional. Therefore, if you are still unsure of how to decide, contact your top listed providers, describe your project, and ask for their suggestions. For example, your project may need stable uptime or high performance; thus, a cloud or dedicated server will be more suitable for you.
The provider should have plenty of experience from several types of infrastructures and projects, saving you a lot of potential issues. Consequently, you can compare all offers and choose the one you are the most interested in.



